cardiovascular system pdf
Cardiovascular System⁚ A Comprehensive Overview
The cardiovascular system‚ also known as the circulatory system‚ is a vital organ system that plays a crucial role in maintaining life. It is responsible for transporting essential substances throughout the body‚ including oxygen‚ nutrients‚ hormones‚ and waste products. This intricate network of blood vessels and the heart works tirelessly to ensure that every cell in the body receives the necessary materials for survival and function.
Introduction
The cardiovascular system‚ often referred to as the circulatory system‚ is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to transport essential substances throughout the body. This vital system is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to every cell‚ while simultaneously removing waste products and carbon dioxide. The heart‚ the central component of this system‚ acts as a powerful pump‚ propelling blood through a vast network of blood vessels. These vessels‚ including arteries‚ veins‚ and capillaries‚ form a closed circuit‚ ensuring continuous circulation of blood and the efficient exchange of vital substances.
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System
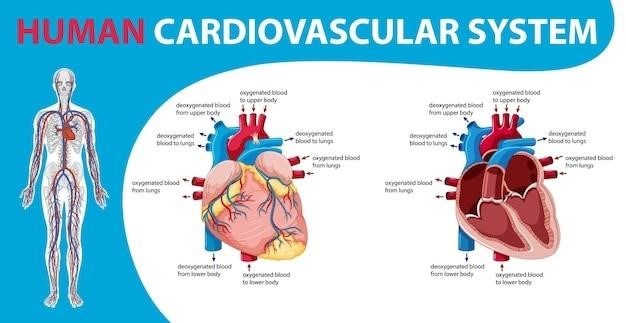
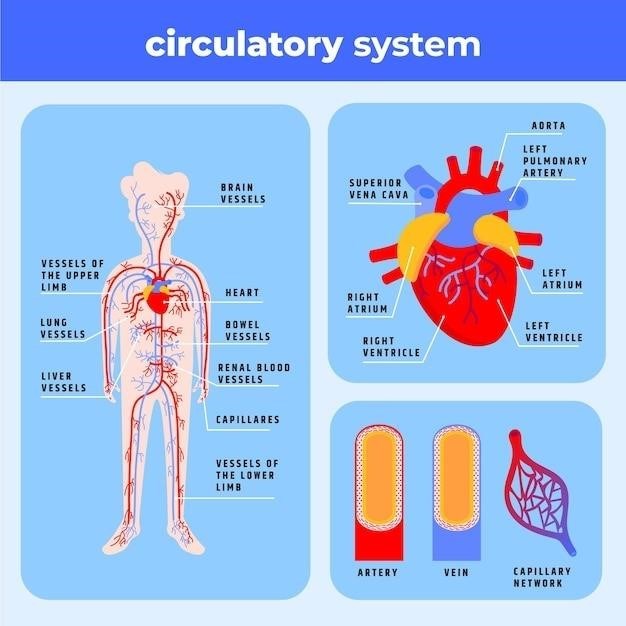
The cardiovascular system is composed of two main components⁚ the heart and the blood vessels. The heart‚ a muscular organ located in the chest‚ is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is divided into four chambers⁚ the right atrium and ventricle‚ and the left atrium and ventricle. Blood enters the heart through the atria and is pumped out by the ventricles. The blood vessels‚ a network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body‚ are classified into three main types⁚ arteries‚ veins‚ and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart‚ while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries‚ the smallest blood vessels‚ connect arteries and veins and facilitate the exchange of oxygen‚ nutrients‚ and waste products between blood and tissues.
The Heart
The heart‚ a four-chambered muscular organ‚ is the central component of the cardiovascular system. It acts as a pump‚ propelling blood throughout the body. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body‚ which is then pumped to the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the left atrium and is then pumped to the left ventricle‚ which propels it to the rest of the body. The heart’s efficient pumping action is facilitated by a specialized conduction system that generates and transmits electrical impulses‚ coordinating the contraction of the heart chambers. These intricate mechanisms ensure the continuous circulation of blood‚ delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels‚ the intricate network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body‚ are essential for the cardiovascular system’s function. Arteries‚ with their thick‚ elastic walls‚ transport oxygenated blood away from the heart. Veins‚ with thinner walls and valves to prevent backflow‚ carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries‚ the smallest and most numerous blood vessels‚ form a network that connects arteries and veins. They are responsible for the vital exchange of gases‚ nutrients‚ and waste products between blood and tissues. The structure and function of these blood vessels are crucial for maintaining blood pressure‚ regulating blood flow‚ and ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body.
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system’s physiology is a complex and fascinating interplay of mechanics and electrical impulses. The heart‚ a powerful pump‚ drives the circulation of blood throughout the body. This continuous movement of blood‚ known as blood circulation‚ is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. The rhythmic contractions of the heart‚ known as the cardiac cycle‚ involve the coordinated actions of the four chambers and valves. This intricate process ensures efficient blood flow through the pulmonary and systemic circuits‚ providing oxygenated blood to the body and returning deoxygenated blood to the lungs for reoxygenation. Understanding the physiology of the cardiovascular system is crucial for comprehending its vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Blood Circulation
Blood circulation is the continuous movement of blood throughout the body‚ driven by the rhythmic contractions of the heart. This vital process ensures that every cell in the body receives a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients‚ while simultaneously removing waste products. The circulatory system is divided into two main circuits⁚ the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit. The pulmonary circuit carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation‚ while the systemic circuit delivers oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. This intricate dance of blood flow is essential for maintaining life‚ ensuring that all organs and tissues function optimally.
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle represents the rhythmic sequence of events that occur with each heartbeat‚ encompassing both contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the heart chambers. This coordinated cycle ensures the efficient pumping of blood throughout the body. During systole‚ the heart chambers contract‚ forcing blood into the arteries. Diastole allows the chambers to relax and refill with blood. The cardiac cycle is regulated by a complex interplay of electrical and mechanical events‚ involving specialized cells within the heart that generate and conduct electrical impulses‚ triggering muscle contractions. The synchronized contractions and relaxations of the heart chambers ensure a continuous and efficient flow of blood‚ essential for sustaining life.
Cardiovascular System Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels‚ posing significant health risks worldwide. These diseases arise from various factors‚ including genetic predisposition‚ lifestyle choices‚ and environmental influences. CVDs can manifest as heart disease‚ stroke‚ peripheral artery disease‚ and other conditions that disrupt the normal function of the cardiovascular system. They can lead to serious complications‚ including heart attacks‚ heart failure‚ and even death. Understanding the risk factors and adopting preventive measures is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and reducing the likelihood of developing these debilitating diseases.
Heart Disease
Heart disease‚ a leading cause of death globally‚ encompasses a spectrum of conditions affecting the heart’s structure and function. Coronary artery disease‚ characterized by the narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup‚ is a common type of heart disease. This narrowing restricts blood flow to the heart muscle‚ leading to chest pain (angina) or a heart attack. Other forms of heart disease include heart valve disorders‚ arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat)‚ and cardiomyopathy (weakening of the heart muscle). These conditions can cause various symptoms‚ including fatigue‚ shortness of breath‚ and swelling in the legs and feet. Early detection and management are crucial for preventing complications and improving outcomes for individuals with heart disease.
Stroke
Stroke‚ a serious medical condition affecting the brain‚ occurs when blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced. This disruption can cause brain cells to die‚ leading to permanent damage and neurological deficits. There are two main types of stroke⁚ ischemic stroke‚ caused by a blood clot blocking an artery in the brain‚ and hemorrhagic stroke‚ caused by a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. Symptoms of stroke can vary depending on the affected area of the brain and include sudden weakness or numbness in the face‚ arm‚ or leg‚ difficulty speaking or understanding speech‚ vision problems‚ and loss of balance or coordination. Prompt medical attention is crucial for minimizing brain damage and improving the chances of recovery.
Maintaining Cardiovascular Health
A healthy cardiovascular system is essential for overall well-being. Maintaining cardiovascular health requires a holistic approach that encompasses both lifestyle modifications and medical management. Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in preventing and managing cardiovascular diseases. These include adopting a balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats‚ cholesterol‚ and sodium; engaging in regular physical activity; maintaining a healthy weight; quitting smoking; and managing stress effectively. Medical management involves working closely with a healthcare professional to address specific risk factors‚ such as high blood pressure‚ high cholesterol‚ and diabetes. Medications‚ if necessary‚ can help control these conditions and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. By taking proactive steps to maintain cardiovascular health‚ individuals can significantly improve their overall well-being and reduce their risk of developing serious heart problems.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. Adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits‚ vegetables‚ whole grains‚ and lean protein can lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Regular physical activity‚ such as brisk walking‚ jogging‚ or swimming‚ strengthens the heart muscle‚ improves blood circulation‚ and helps maintain a healthy weight. Quitting smoking is essential as it significantly reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke. Managing stress through techniques like yoga‚ meditation‚ or deep breathing exercises can lower cortisol levels‚ which can contribute to cardiovascular problems. These lifestyle changes‚ when implemented consistently‚ can significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and contribute to a healthier life.
Medical Management
Medical management plays a vital role in preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases. Regular checkups with a healthcare professional are essential for monitoring blood pressure‚ cholesterol levels‚ and overall cardiovascular health. For individuals with high blood pressure‚ medications like ACE inhibitors‚ beta-blockers‚ or calcium channel blockers can effectively lower blood pressure. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol levels‚ while blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin can reduce the risk of blood clots. In cases of heart failure‚ medications like digoxin or diuretics can help improve heart function and reduce fluid buildup. For individuals with arrhythmias‚ pacemakers or defibrillators may be implanted to regulate heart rhythm. Early detection and appropriate medical management can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with cardiovascular diseases.
The cardiovascular system is a complex and vital organ system that plays a crucial role in maintaining life. Understanding its anatomy‚ physiology‚ and common diseases is essential for promoting cardiovascular health. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits‚ such as regular exercise‚ a balanced diet‚ and stress management‚ individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Early detection and appropriate medical management are crucial for individuals diagnosed with cardiovascular conditions. With a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications‚ medical interventions‚ and ongoing monitoring‚ individuals can maintain a healthy cardiovascular system and enjoy a longer‚ healthier life.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.